Introduction to NURBS Surface Fill Holes function module and library function API description
Introduction to NURBS Surface Fill Holes Function Module
Download the stand-alone application for testing this feature from here. Find the following GUI in the application for this feature.
![]()
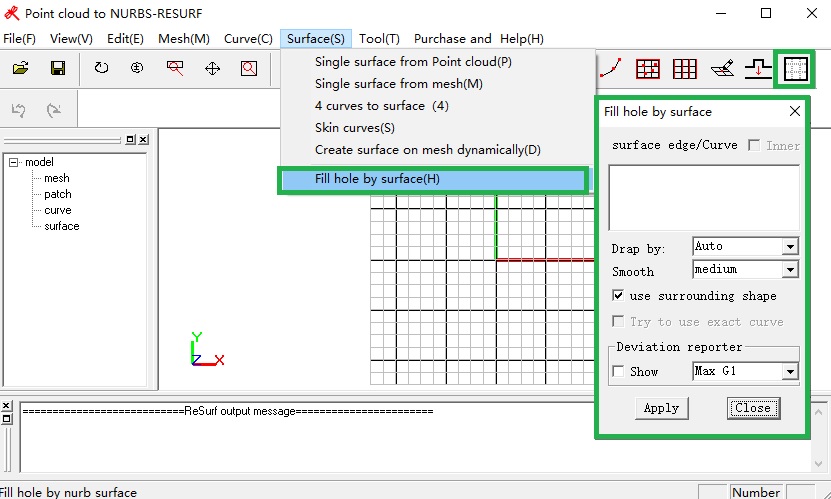
The feature is encapsulated in a package called ResurfNurbs. For the phenomenon of holes or defects in some geometries, the ResurfNurbs library function provides the function of compensating for the defects of holes with NURBS surfaces. After the NURBS surface fills the hole, it reaches G1 continuous at the hole boundary. The ResurfNubbs library function provides a continuous numerical report of G0/G1.
Figure 1 below is a geometric model with holes :
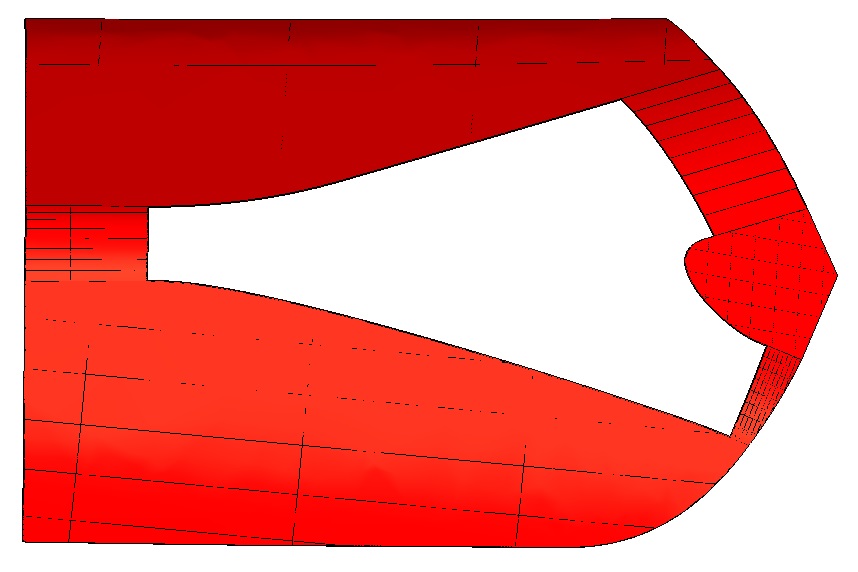
( Figure 1 )
Fig. 2 Pick up the blue hole boundary line as the input parameter to generate the NURBS surface :
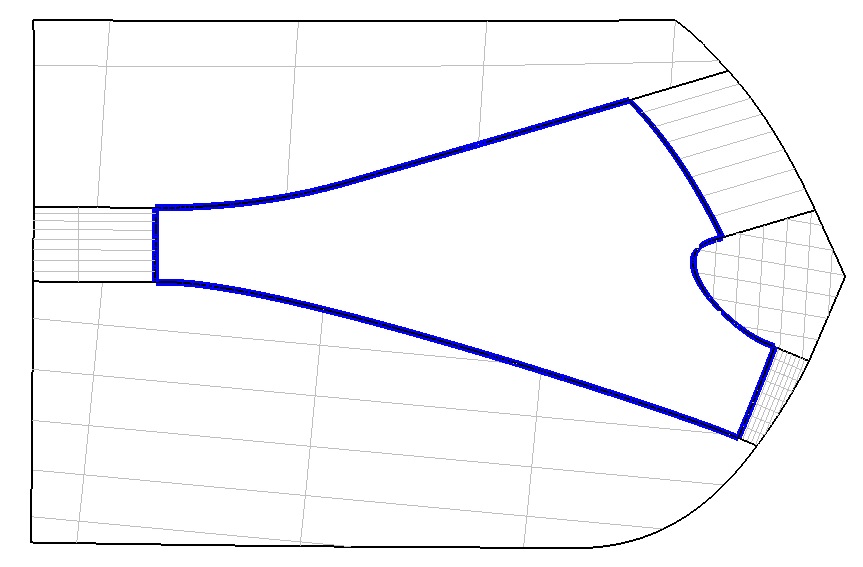
(Figure 2)
Figure 3 generates a clipped NRUBS surface fill hole :
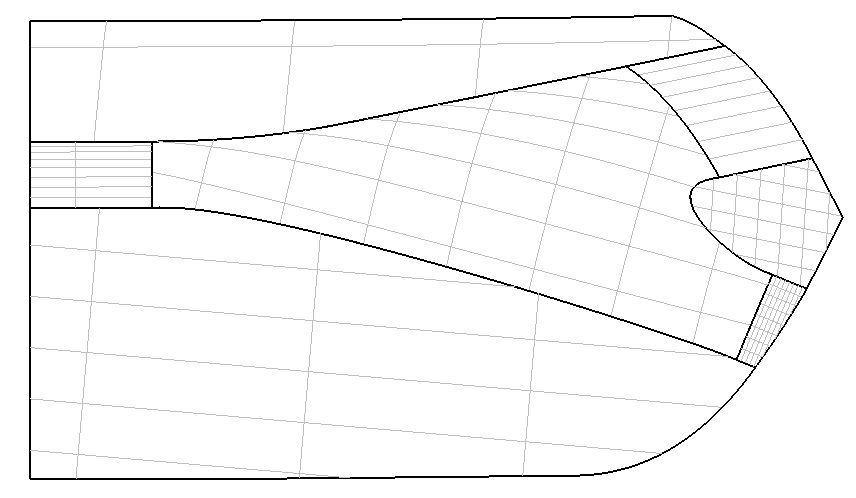
(Figure 3)
Figure 4 shows the G1 continuity deviation report of the hole NURBS and the adjacent NURBS surface on the common boundary line:
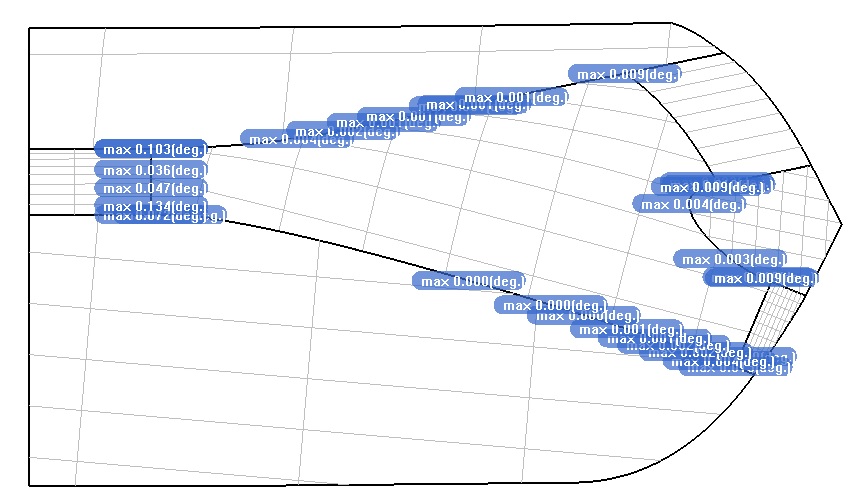
(Figure 4)
The ResurfNurbs library function can generate both clipped surface fill holes and non-clipped quad surface fill holes. Specifically filling holes with that type of surface, the user can choose based on the shape of the hole boundary.
API Call
Calling the API must be strictly enforced in the following form:
Step 1: Initialization . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_Start() for initialization;
Step 2: Enter the boundary line . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_AppendBoundaryCurve() to add a 3D curve or RsFillHoleByNurbs_AppendSurfaceEdge() to add a surface boundary line. These boundary lines must be enclosed in a closed loop, and their end-to-end distance from end to end should not be too large.
Step 3: Parameter settings . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_SetSmoothFactor() to set the surface smoothness.
Step 4: Set the parameters . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_SetDrapSurfaceType() to set the shape type of the surface;
Step 5: Generate Surface . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_DoFill() to perform surface generation;
Step 6: Get the generated surface data . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetNurbs() to get the resulting NURBS surface;
Step 7: If the crop surface is generated, get the data of the clipping boundary curve . Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get2DTrimmingCurveCount() to get the number of boundary curves on the clipping ring; Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get2DTrimmingCurve() to get the data for the ith 2D clipping boundary line; Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get3DTrimmingCurve() to get the data for the ith 3D cropped boundary line;
Step 8: Get the report for the coninuity on the new surface edge. Call RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetMaxG1ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** angles, int* point_num); RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetG1ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** angles, int* point_num); RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetMaxG0ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** deviation, int* point_num); RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetG0ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** deviation, int* point_num); checkG0/G1 continuity on surface edges.
Step9 : End calling. RsFillHoleByNurbs_End() .
API parameter description
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_Start();
Function : Initialize the function. This interface is the function that must be called first .
Parameters : The interface has no parameters.
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_AppendBoundaryCurve(double* cpx, double* cpy, double* cpz, double* weight, int ctrlp_num, int is_rational, int degree, double* knot);
Function : Add a 3D NURBS curve as a boundary line. A 3D NURBS curve is a spatial curve that is not on a surface.
Input parameter description :
- int ctrlp_num : the number of control points of the curve ;
- int is_rational: Whether the curve is a rational NURBS curve. 0 represents a non-rational B-spline curve; 1 represents a rational NURBS curve ;
- int degree : the number of degree for the curve; the inequality ctrlp_num>=(degree+1) must be satisfied; when ctrlp_num==(degree+1), the curve is a Bezier curve ;
- double* knot : The node vector of the curve. The length is ctrlp_num+degree+1 ;
- double* cpx : Stores the x coordinates of the curve control vertices with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double* cpy: stores the y-coordinate of the curve-controlled vertice, with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double* cpz: stores the z-coordinates of the curve control vertices, with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double* weight: Stores the weight of the curve control vertice, with a length of ctrlp_num; If the curve is a non-rational B spline, the weight can be empty ;
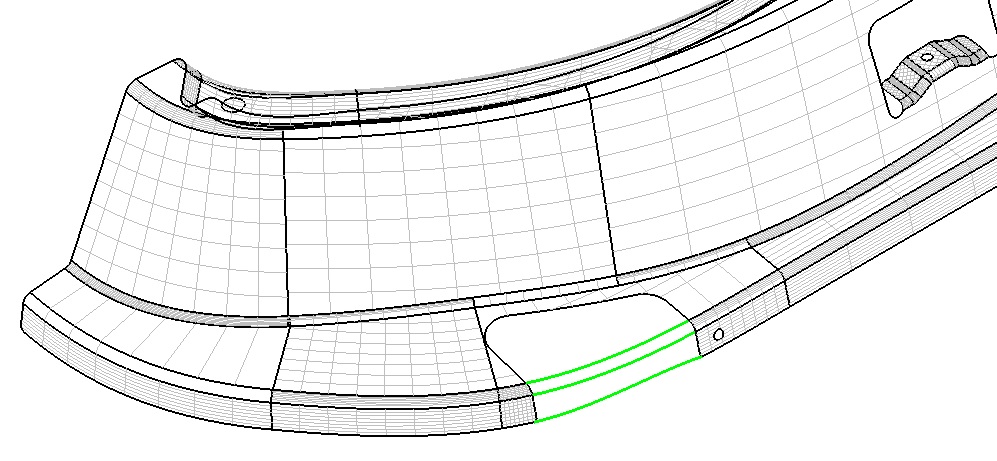
( Figure 5. Green is a 3D curve )
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_AppendSurfaceEdge(double* cpu, double* cpv, double* curve_weight, int ctrlp_num, int is_curve_rational, int degree, double* knot,int iso_type, int continuity, int hasface, double* surf_cpx, double* surf_cpy, double* surf_cpz, double* surf_weight, int u_num, int v_num, int is_surf_rational, int u_degree, int v_degree, double* u_knot, double* v_knot);
Function : Add a surface edge as a boundary line. A surface edge is a curve that falls on a surface, defined by a two-dimensional curve on a surface's 2D parameter space.
Input parameter description :
The parameter contains two parts: NURBS surface data and surface boundary curve data.
NURBS Surface Data :
- int u_num : the number of control points of the surface in the U direction ;
- int v_num: the number of control points of the surface in the V direction ;
- int u_degree: the number of degree the surface is in the U direction ;
- int v_degree: the number of degree the surface is in the U direction;
- int is_surf_rational: Whether the surface is a rational NURBS surface. 0 represents the non-rational B spline surface; 1 represents a rational NURBS surface ;
- double* u_knot: The node vector of the surface in the U direction, with a length of u_num+u_degree+1
- double* v_knot: The node vector of the surface in the V direction, with a length of v_num+v_degree+1
- double* surf_cpx: The x-component coordinates of the surface control point, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
- double* surf_cpy: the y-component coordinates of the surface control point, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
- double* surf_cpz: The z-component coordinates of the surface control point, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
- double* surf_weight: Weights on surface control points, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction; If the surface is a non-rational B spline , the value can be null ;
Data of surface boundary curves
- int ctrlp_num : the number of control points of the curve ;
- int is_curve_rational: Whether the curve is a rational NURBS curve. 0 represents an irrational B-spline ; 1 represents the rational NURBS curve ;
- int degree : the number of degree for the curve; the inequality ctrlp_num>=(degree+1) must be satisfied; when ctrlp_num==(degree+1), the curve is a Bezier curve ;
- double* knot : The knot vector of the curve. The length is ctrlp_num+degree+1 ;
- double* cpu : Stores the U-direction coordinates of the curve control vertices with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double* cpv: stores the v-coordinates of the curve-controlled vertices with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double* curve_weight: Stores the weight of the curve control vertice, with a length of ctrlp_num; If the curve is a non-rational B-spline, then curve_weight can be null;
- int iso_type:
Is the curve an isoparameter line
:
- -1 : The curve is 3D without surface information ;
- 0 : non-isoparameter ;.
- 1: x_iso;
- 2: y_iso;
- 3: west_iso; u= the starting point in u-direction
- 4: south_iso; v=the starting point in v-direction
- 5: east_iso; u=the end point in u-direction
- 6: north_iso; v=the end point in v-direction
- int continuity: the continuity of the new surface on the curve , 0: G0; 1: G1
- int hasface: This value is always 1
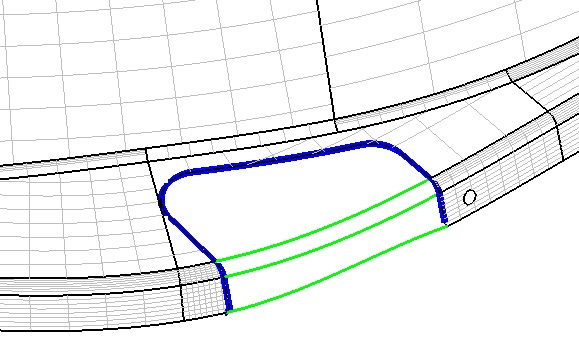
( Figure 6. Blue is the surface edge )
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_SetSmoothFactor(double factor);
Function : Control the smoothness of new surfaces .
Input parameter description :
double factor : [0.0001,1.0], the larger the surface, the smoother it is ;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void void RsFillHoleByNurbs_SetDrapSurfaceType(int type);
Function: Set the stretch form of the surface, and set whether the surface is a cropped surface according to the value of the stretch form.
Input parameter description:
int type:
- 0 --- Automatically calculate the stretch and generate the clipping surface
- 1 ---- Stretch along the x-axis to create a clipped surface
- 2 ---- Stretch along the y-axis to create a clipped surface
- 3 ---- Stretch along the z-axis to create a clipping surface
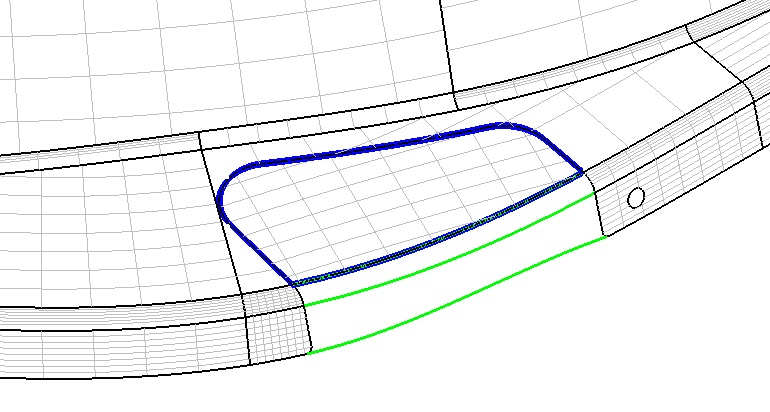
( Figure 7. Fill the holes with clipped surfaces in the blue curve )
- 4 ---- Stretch the four boundary lines to generate a non-clipping surface. The program automatically calculates 4 corners.
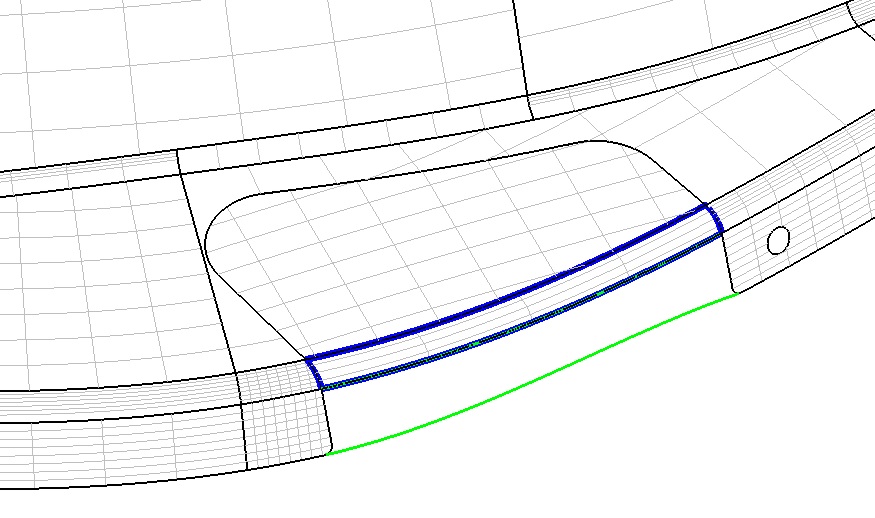
( Figure 8. Inside the blue curve is filled with a non-clipping surface )
- 5 ---- Stretching the four boundary lines to generate the first type of coons non-clipping surface. The program automatically calculates 4 corners.
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_DoFill();
Function: Perform surface generation.
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) bool RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetNurbs(int* u_num, int* v_num, int* u_degree, int* v_degree, double** u_knot, double** v_knot, double** cpx, double** cpy, double** cpz);
Function: Get data for new NURBS surfaces.
Output parameter description:
- int *u_num : the number of control points of the surface in the U direction ;
- int *v_num: the number of control points of the surface in the V direction ;
- int *u_degree: the number of degree the surface is in the U direction ;
- int *v_degree: the number of degree the surface is in the V direction;
- double** u_knot: the knot vector of the surface in the U direction, the length is u_num+u_degree+1 ;
- double** v_knot: the knot vector of the surface in the V direction, the length is v_num+v_degree+1 ;
- double** cpx: the x-component coordinates of the surface control point, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
- double** cpy: The y-component coordinates of the surface control point, with a length of u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
- double** cpz: the z-component coordinates of the surface control point, the length is u_num*v_num, arranged in the v direction ;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) int RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get2DTrimmingCurveCount();
Function: Returns how many boundary lines the new clipping surface consists of. If the new surface is a non-clipping surface, this number is 0. If it is a clipping surface, these boundary curves form a bounding ring. Each boundary curve can be taken from a 2D curve on the parameter domain and a 3D curve on the physical surface position.
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get2DTrimmingCurve(int index, int* ctrlp_num, int* degree, double** knot, double** cpu, double** cpv);
Function: Given an index, take out the index 2D curve data on the boundary ring.
Output parameter description:
Data of surface boundary curves :
- int index: the id number of the curve on the boundary ring ;
- int *ctrlp_num : Number of control points of the curve ;
- int *degree :degree of the curve;
- double** knot : The knot vector of the curve. The length is ctrlp_num+degree+1 ;
- double** cpu : Stores the U-direction coordinates of the curve control vertices, with a length of ctrlp_num ;
- double** cpv: stores the V-coordinates of the curve control vertices with a length of ctrlp_num ;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_Get3DTrimmingCurve(int index, int* ctrlp_num, int* degree, double** knot, double** cpx, double** cpy, double** cpz);
Function: Given an index, retrieve the index 3D curve data on the bounding ring.
Output parameter description:
Data of surface boundary curves :
- int index: the id number of the curve on the boundary ring;
- int *ctrlp_num : Number of control points of the curve;
- int *ctrlp_num : Number of control points of the curve;
- int *degree : the number of curves;
- double** knot : The node vector of the curve. The length is ctrlp_num+degree+1;
- double** cpx : Stores the x-component coordinates of the curve control vertices with a length of ctrlp_num;
- double** cpy : Stores the y-component coordinates of the curve control vertices with a length of ctrlp_num;
- double** cpz : stores the z-component coordinates of the curve control vertice, with a length of ctrlp_num;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_End();
Function: End surface generation 。
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_Clear();
Function: Erase all data, reset .
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) bool RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetStatus();
Function: See if the surface is successfully generated.
Return value :
- true : The NURBS surface was successfully generated ;
- false : No surface is generated ;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetMaxG1ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** angles, int* point_num);
Function: Reports the maximum G1 continuous deviation angle on each boundary line in the state of successful surface generation. If the boundary line is a surface curve, there is a continuous angular deviation value of G1. If the boundary line is a 3D curve, there is no G1 continuous angular deviation value.
Output parameter description:
- double** point_x : The x-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G1 continuous angular deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_y : the y-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G1 continuous angular deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_z : The z-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G1 continuous angular deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** deviation : the G0 continuous deviation distance value of the point where the maximum G1 continuous angular deviation value is located on the boundary line. The array size is *point_num;
- int* point_num : can measure the number of continuous boundary lines in G1;
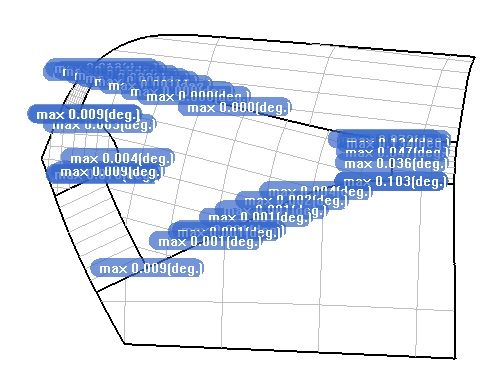
( Figure 9)
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetG1ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** angles, int* point_num);
Function: Reports the maximum G1 continuous deviation angle of a batch of discrete points on the surface boundary line when the surface is successfully generated. If the input boundary line is a surface curve, there is a continuous angular deviation value of G1; If the input boundary line is a 3D curve, there is no G1 continuous angular deviation value.
Output parameter description:
- double** point_x : The x-coordinate component of the point where the continuous angular deviation value of G1 is located on the boundary line, and the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_y : The y-coordinate component of the point where the continuous angular deviation value of G1 is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_z : The z-coordinate component of the point where the continuous angular deviation value of G1 is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** deviation : the G0 continuous deviation distance value of the point where the G1 continuous angular deviation value is located on the boundary line. The array size is *point_num;
- int* point_num : the number of discrete points on the boundary line;
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetMaxG0ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** deviation, int* point_num);
Function: Reports the maximum G0 continuous distance deviation on each boundary line in the state of successfully generating the surface. Each boundary line of the surface, whether it is a surface curve or a 3D curve, has a G0 continuous distance deviation value.
Output parameter description:
- double** point_x : the x-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_y : The y-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_z : The z-coordinate component of the point where the maximum G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, and the array size is *point_num;
- double** deviation : The G0 continuous deviation distance value of the point where the maximum G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line. The array size is *point_num;
- int* point_num : Measures the number of continuous boundary lines of G0;
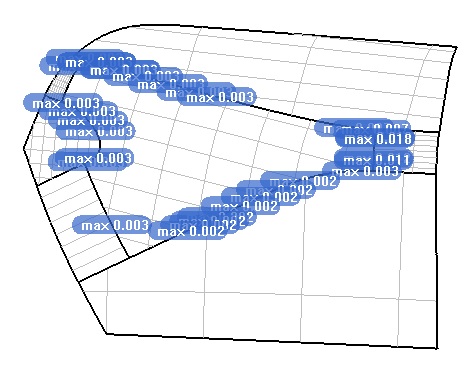
(Figure 10)
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) void RsFillHoleByNurbs_GetG0ReportData(double** point_x, double** point_y, double** point_z, double** deviation, int* point_num);
Function: Reports the G0 continuous distance deviation of a batch of discrete points on the boundary line in the state of successfully generating the surface. Each boundary line of the surface, whether it is a surface curve or a 3D curve, has a G0 continuous distance deviation value.
Output parameter description:
- double** point_x : the x-coordinate component of the point where the G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_y : The y-coordinate component of the point where the G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** point_z : The z-coordinate component of the point where the G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line, the array size is *point_num;
- double** deviation : The G0 continuous deviation distance value of the point where the G0 continuous distance deviation value is located on the boundary line. The array size is *point_num;
- int* point_num : The number of discrete points in the batch;